Volume Size
In this section, you’ll have a better understanding of concepts related to volume size.
Volume Size:
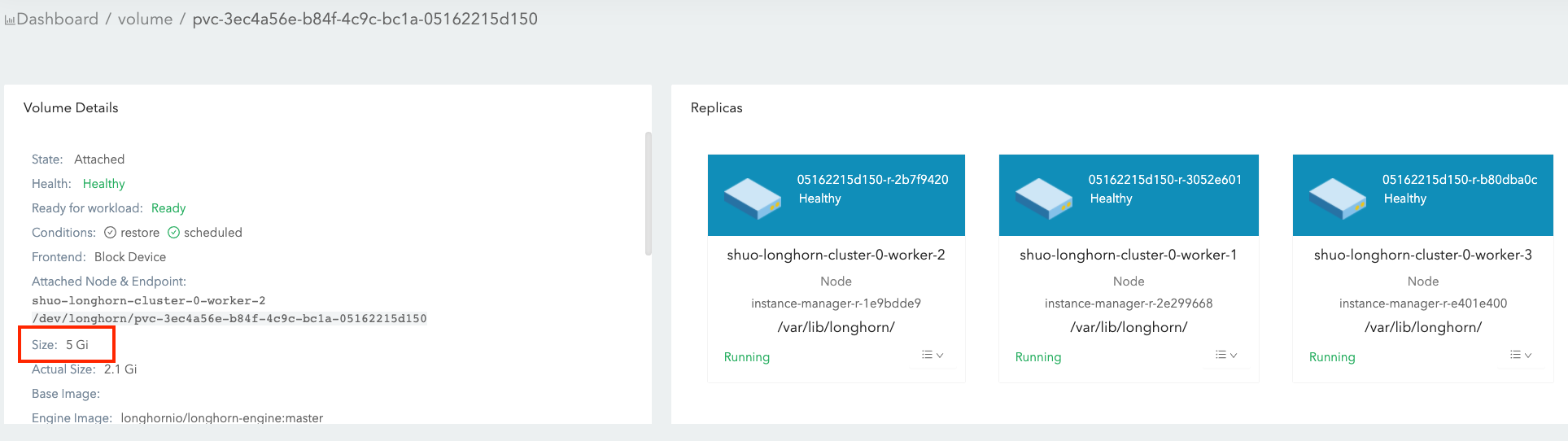
- It is what you set during the volume creation, and we will call it nominal size in this doc to avoid ambiguity.
- Since the volume itself is just a CRD object in Kubernetes and the data is stored in each replica, this is actually the nominal size of each replica.
- The reason we call this field as “nominal size” is that Longhorn replicas are using sparse files to store data and this value is the apparent size of the sparse files (the maximum size to which they may expand). The actual size used by each replica is not equal to this nominal size.
- Based on this nominal size, the replicas will be scheduled to those nodes that have enough allocatable space during the volume creation. (See this doc for more info about node allocation size.)
- The value of nominal size determines the max available space when the volume is in use. In other words, the current active data size hold by a volume cannot be greater than its nominal size.
Volume Actual Size

- The actual size indicates the actual space used by each replica on the corresponding node.
- Since all historical data stored in the snapshots and active data will be calculated into the actual size, the final value can be greater than the nominal size.
- The actual size will be shown only when the volume is running.
Example
In the example, we will explain how volume size and actual size get changed after a bunch of IO and snapshot related operations.
The illustration presents the file organization of one replica. The volume head and snapshots are actually sparse files, which we mentioned above.
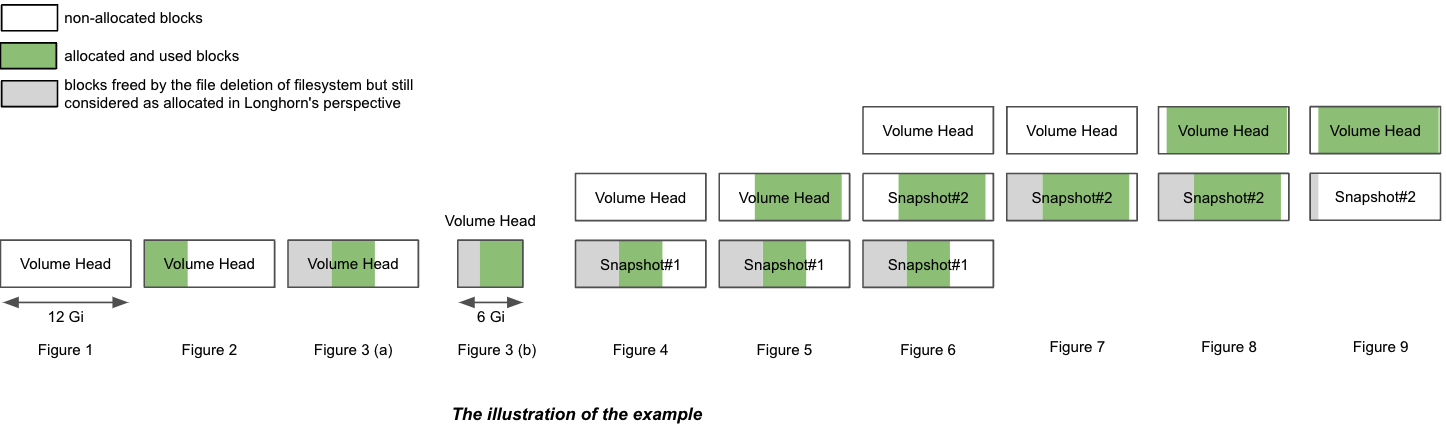
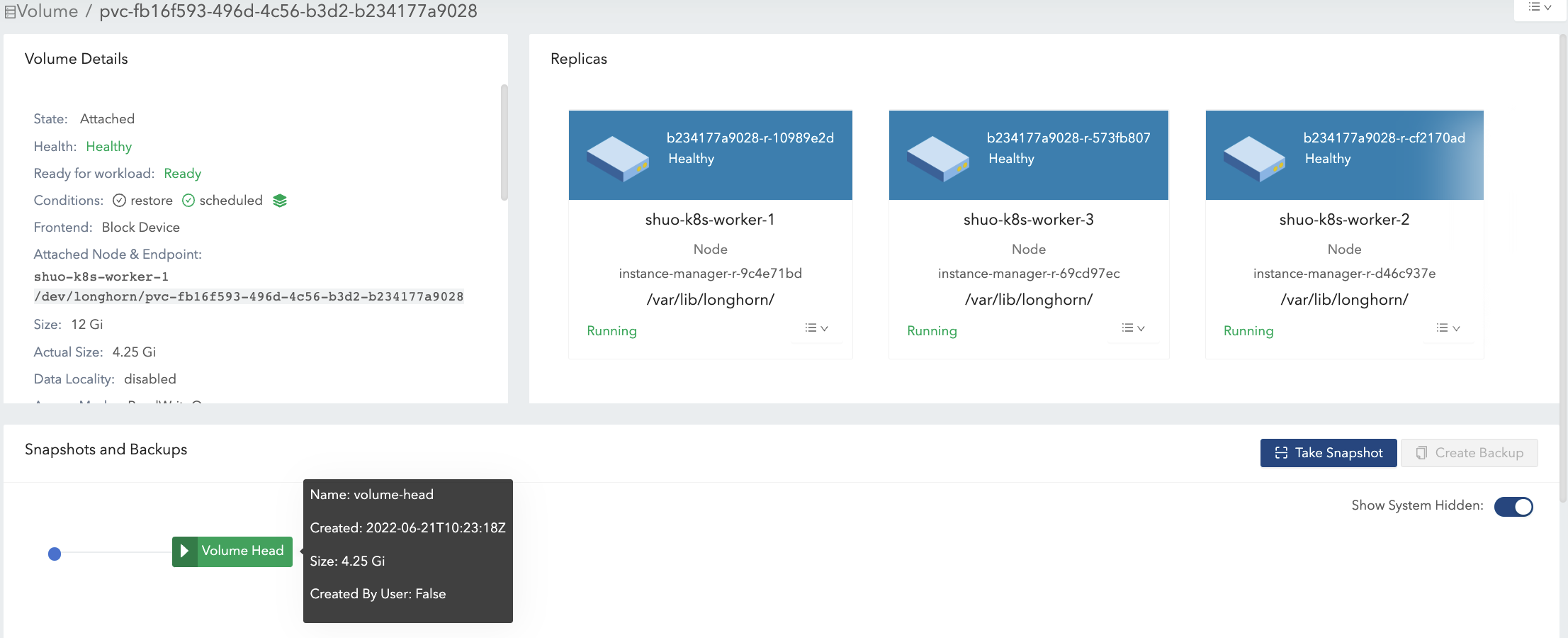
- Create a 12 Gi volume with a single replica, then attach and mount it on a node. See Figure 1 of the illustration.
- For the empty volume, the nominal
sizeis 12 Gi and theactual sizeis almost 0. - There is some meta info in the volume hence the
actual sizeis 0.25 Gi and is not exactly 0.
- For the empty volume, the nominal

- Write 4 Gi data (data#0) in the volume mount point. The
actual sizeis increased by 4 Gi because of the allocated blocks in the replica for the 4 Gi data. Meanwhile,dfcommand in the filesystem also shows the 4 Gi used space. See Figure 2 of the illustration.
Delete the 4 Gi data. Then,
dfcommand shows that the used space of the filesystem is nearly 0, but theactual sizeis unchanged.Users can see the volume
actual sizeis not shrunk after deleting the 4 Gi data. Longhorn is a block-level storage system. Therefore, the deletion in the filesystem only marks the blocks that belong to the deleted file as unused. Currently, Longhorn does not support TRIM/UNMAP operations, so thediscardmount option orfstrimin the filesystem layer cannot reclaim the unused blocks. In consequence, the actual size of Longhorn volumes cannot be shrunk in this case.

Then, rewrite the 4 Gi data (data#1), and the
dfcommand in the filesystem shows 4 Gi used space again. However, theactual sizeis increased by 4 Gi and becomes 8.25Gi. See Figure 3(a) of the illustration.After deletion, filesystem may or maynot reuse the recently freed blocks from recently deleted files according to the filesystem design and please refer to Block allocation strategies of various filesystems. If the volume nominal
sizeis 12 Gi, theactual sizein the end would range from 4 Gi to 8 Gi since the filesystem may or maynot reuse the freed blocks. On the other hand, if the volume nominalsizeis 6 Gi, theactual sizeat the end would range from 4 Gi to 6 Gi, because the filesystem has to reuse the freed blocks in the 2nd round of writing. See Figure 3(b) of the illustration.Thus, allocating an appropriate nominal
sizefor a volume that holds heavy writing tasks according to the IO pattern would make disk space usage more efficient.
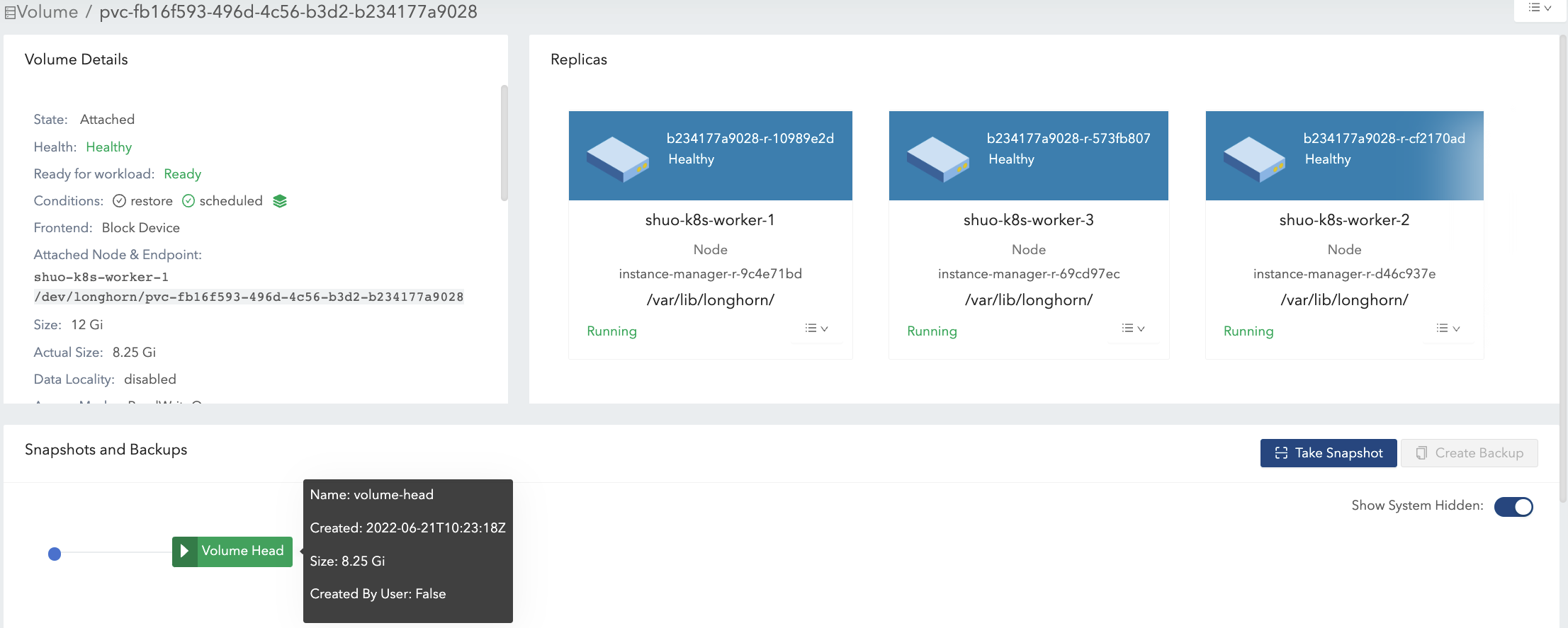
- Take a snapshot (snapshot#1). See Figure 4 of the illustration.
- Now data#1 is stored in snapshot#1.
- The new volume head size is almost 0.
- With the volume head and the snapshot included, the
actual sizeremains 8.25 Gi.

Delete data#1 from the mount point.
- The data#1 filesystem level removal info is stored in current volume head file. For snapshot#1, data#1 is still retained as the historical data.
- The
actual sizeis still 8.25 Gi.
Write 8 Gi data (data#2) in the volume mount, then take one more snapshot (snapshot#2). See Figure 5 of the illustration.
- Now the
actual sizeis 16.3 Gi, which is greater than the volume nominalsize. - From a filesystem’s perspective, the overlapping part between the two snapshots is considered as the blocks that have to be reused or overwritten. But in terms of Longhorn, these blocks are actually fresh ones held in another snapshot/volume head. See the 2 snapshots in Figure 6.
The volume head holds the latest data of the volume only, while each snapshot may store historical data as well as active data, which consumes at most size space. Therefore, the volume
actual size, which is the size sum of the volume head and all snapshots, is possibly bigger than the size specified by users.Even if users will not take snapshots for volumes, there are operations like rebuilding, expansion, or backing up that would lead to system (hidden) snapshot creation. As a result, volume
actual sizebeing larger than size is unavoidable under some use cases.- Now the
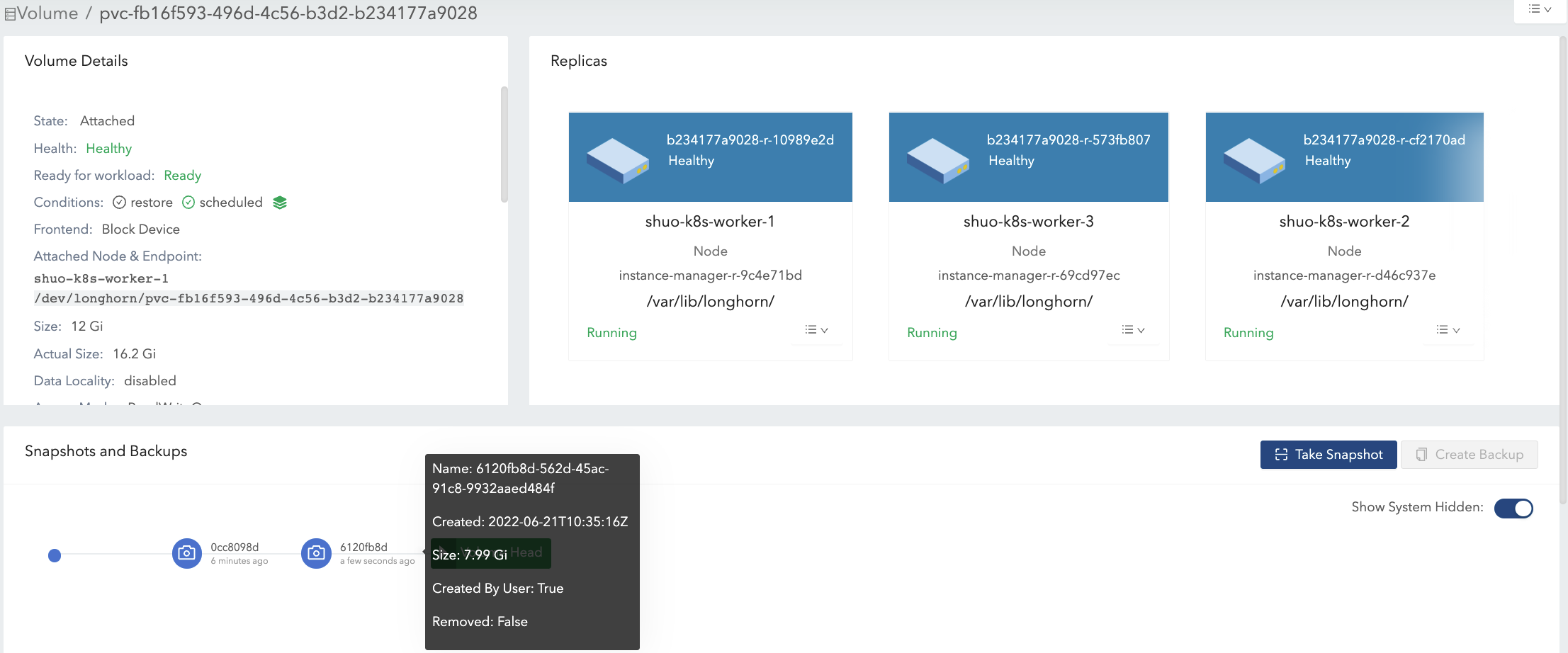
- Delete snapshot#1 and wait for snapshot purge complete. See Figure 7 of the illustration.
- Here Longhorn actually coalesces the snapshot#1 with the snapshot#2.
- For the overlapping part during the coalesce, the newer data (data#2) will be retained in the blocks. Then some historical data is removed and the volume gets shrunk (from 16.3 Gi to 11.4 Gi in the example).
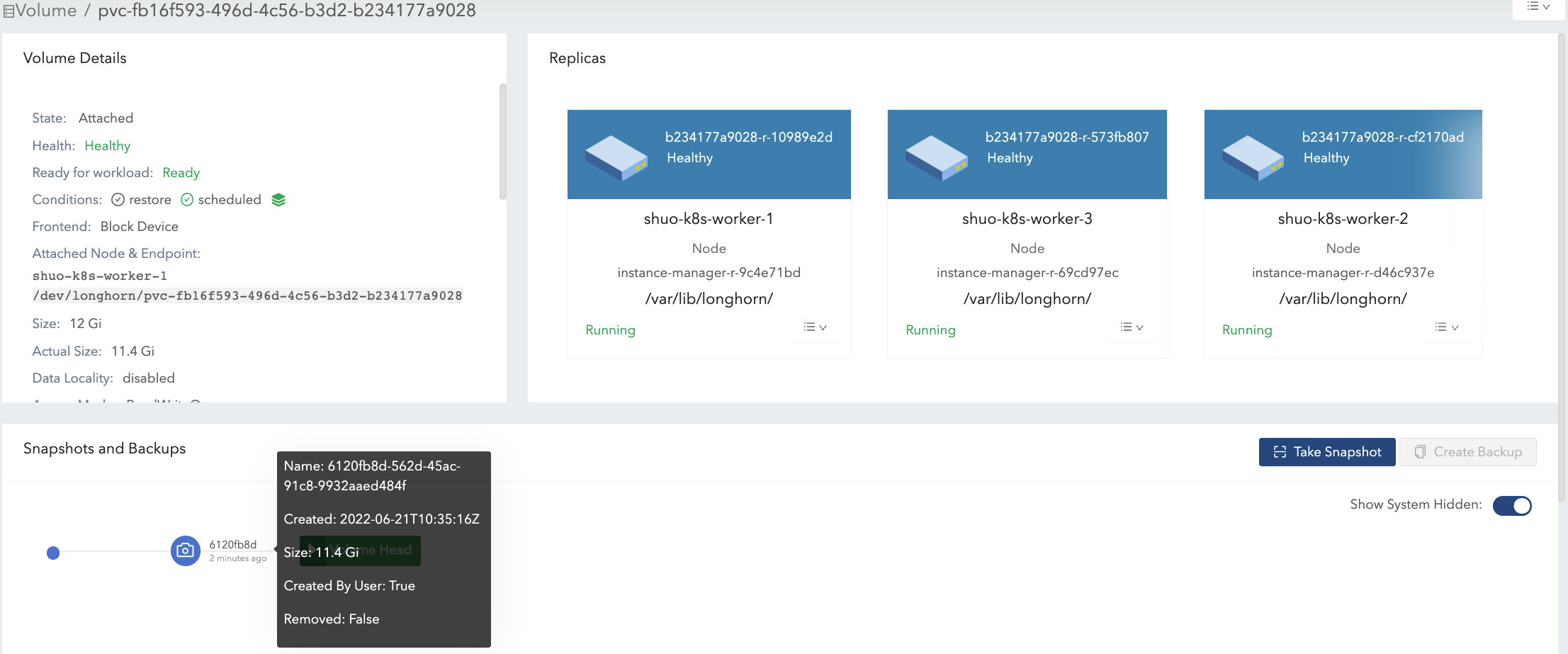
Here we summarize the important things related to disk space usage we have in the example:
Unused blocks are not released
Longhorn does not support TRIM/UNMAP operations. Hence deleting files from filesystems will not lead to volume actual size decreasing/shrinking.
Allocated blocks but unused are not reused
Deleting then writing new files would lead to the actual size keeps increasing. Since the filesystem may not reuse the recently freed blocks from recently deleted files. Thus, allocating an appropriate nominal size for a volume that holds heavy writing tasks according to the IO pattern would make disk space usage more efficient.
By deleting snapshots, the overlapping part of the used blocks might be eliminated regardless of whether the blocks are recently released blocks by the filesystem or still contain historical data.
Space Configuration Suggestions for Volumes
Reserve enough free space in disks as buffers in case of the actual size of existing volumes keep growing up.
A quick estimation for maximum space consumption estimation of a volume is
(N + 1 + 1) x head/snapshot average actual sizewhere N is the number of snapshots retained, the 1st 1 is for the system snapshot, and the 2nd 1 is for the temporary space that may be required by snapshot deletion.
If there are heavy writing tasks for volumes, the head/snapshot average actual size would be volume the nominal size. In this case, it’s better to set
Storage Over Provisioning Percentageto be smaller than 100% to avoid disk space exhaustion.
Do not retain too many snapshots for the volumes.
Cleaning up snapshots will help reclaim disk space. There are two ways to clean up snapshots:
- Delete the snapshots manually via Longhorn UI.
- Set a snapshot recurring job with retention 1, then the snapshots will be cleaned up automatically.
Also, notice that the extra space, up to volume nominal
size, is required during snapshot cleanup and merge.An appropriate the volume nominal
sizeaccording to the workloads.
© 2019-2026 Longhorn Authors | Documentation Distributed under CC-BY-4.0
© 2026 The Linux Foundation. All rights reserved. The Linux Foundation has registered trademarks and uses trademarks. For a list of trademarks of The Linux Foundation, please see our Trademark Usage page.