Install as a Rancher Apps & Marketplace
Run Longhorn on Kubernetes with Rancher 2.x
One benefit of installing Longhorn through Rancher Apps & Marketplace is that Rancher provides authentication to the Longhorn UI.
If there is a new version of Longhorn available, you will see an Upgrade Available sign on the Apps & Marketplace page. You can click Upgrade button to upgrade Longhorn manager. See more about upgrade here.
Prerequisites
Each node in the Kubernetes cluster where Longhorn is installed must fulfill these requirements.
Longhorn Command Line Tool can be used to check the Longhorn environment for potential issues.
Installation
Note:
- For Kubernetes < v1.25, if your cluster still enables Pod Security Policy admission controller, set
Other Settings > Pod Security Policytotrueto installlonghorn-pspPodSecurityPolicy resource which allows privileged Longhorn pods to start.
- Optional: If Rancher version is 2.5.9 or before, we recommend creating a new project for Longhorn, for example,
Storage. - Navigate to the cluster where you will install Longhorn.

- Navigate to the
Apps & Marketplacepage.
- Find the Longhorn item in the charts and click it.
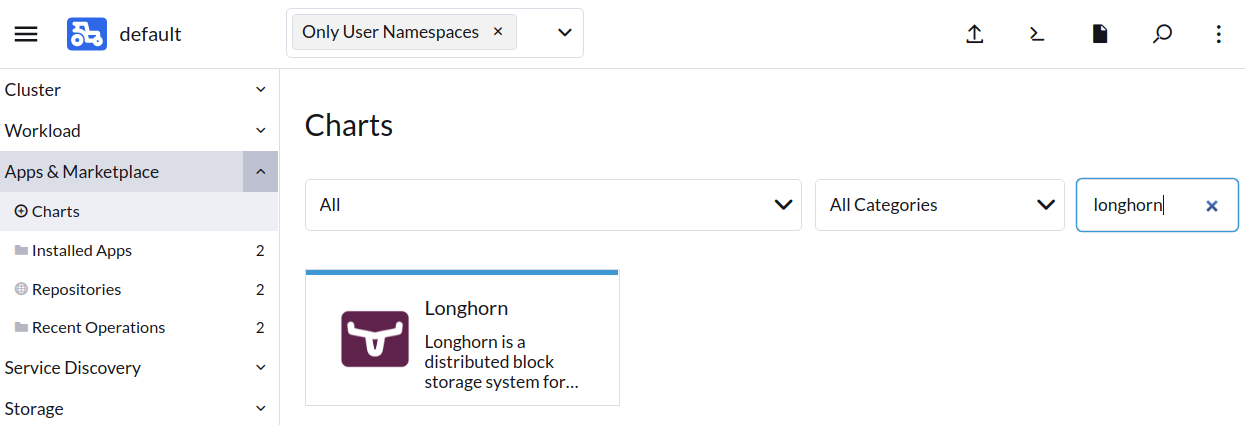
- Click Install.

- Optional: Select the project where you want to install Longhorn.
- Optional: Customize the default settings.
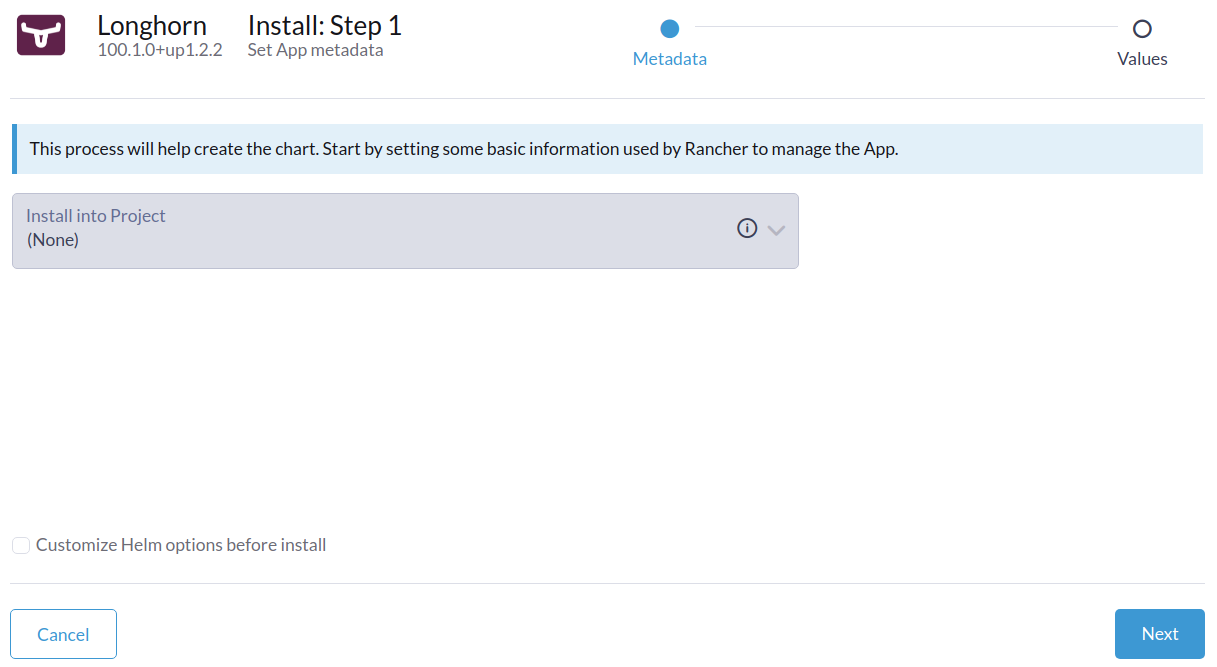
- Click Next. Longhorn will be installed in the longhorn-system namespace.

- Click the Longhorn App Icon to navigate to the Longhorn dashboard.

After Longhorn has been successfully installed, you can access the Longhorn UI by navigating to the Longhorn option from Rancher left panel.
Access UI With Network Policy Enabled
Note that when the Network Policy is enabled, access to the UI from Rancher may be restricted.
Rancher interacts with the Longhorn UI via a service called remotedialer, which facilitates connections between Rancher and the downstream clusters it manages. This service allows a user agent to access the cluster through an endpoint on the Rancher server. Remotedialer connects to the Longhorn UI service by using the Kubernetes API Server as a proxy.
However, when the Network Policy is enabled, the Kubernetes API Server may be unable to reach pods on different nodes. This occurs because the Kubernetes API Server operates within the host’s network namespace without a dedicated per-pod IP address. If you’re using the Calico CNI plugin, any process in the host’s network namespace (such as the API Server) connecting to a pod triggers Calico to encapsulate the packet in IPIP before forwarding it to the remote host. The tunnel address is chosen as the source to ensure the remote host knows to encapsulate the return packets correctly.
In other words, to allow the proxy to work with the Network Policy, the Tunnel IP of each node must be identified and explicitly permitted in the policy.
You can find the Tunnel IP by:
$ kubectl get nodes -oyaml | grep "Tunnel"
projectcalico.org/IPv4VXLANTunnelAddr: 10.42.197.0
projectcalico.org/IPv4VXLANTunnelAddr: 10.42.99.0
projectcalico.org/IPv4VXLANTunnelAddr: 10.42.158.0
projectcalico.org/IPv4VXLANTunnelAddr: 10.42.80.0
Next, permit traffic in the Network Policy using the Tunnel IP. You may need to update the Network Policy whenever new nodes are added to the cluster.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: longhorn-ui-frontend
namespace: longhorn-system
spec:
podSelector:
matchLabels:
app: longhorn-ui
policyTypes:
- Ingress
ingress:
- from:
- ipBlock:
cidr: 10.42.197.0/32
- ipBlock:
cidr: 10.42.99.0/32
- ipBlock:
cidr: 10.42.158.0/32
- ipBlock:
cidr: 10.42.80.0/32
ports:
- port: 8000
protocol: TCP
Another way to resolve the issue is by running the server nodes with egress-selector-mode: cluster. For more information, see RKE2 Server Configuration Reference and K3s Control-Plane Egress Selector configuration.
© 2019-2025 Longhorn Authors | Documentation Distributed under CC-BY-4.0
© 2025 The Linux Foundation. All rights reserved. The Linux Foundation has registered trademarks and uses trademarks. For a list of trademarks of The Linux Foundation, please see our Trademark Usage page.