Backing Image Encryption
Starting with v1.7.0, Longhorn allows you to encrypt and decrypt a backing image by cloning it. The backing image encryption mechanism utilizes the Linux kernel module dm_crypt and the command-line utility cryptsetup.
Clone a Backing Image
You can clone a backing image using YAML code. Notice that, this will create a whole new backing image with the same content as the original one. The backing image also consumes the disk space.
Example of a downloaded backing image:
apiVersion: longhorn.io/v1beta2
kind: BackingImage
metadata:
name: parrot
namespace: longhorn-system
spec:
sourceType: download
sourceParameters:
url: https://longhorn-backing-image.s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/parrot.raw
checksum: 304f3ed30ca6878e9056ee6f1b02b328239f0d0c2c1272840998212f9734b196371560b3b939037e4f4c2884ce457c2cbc9f0621f4f5d1ca983983c8cdf8cd9a
Example of YAML code used to clone the sample backing image:
apiVersion: longhorn.io/v1beta2
kind: BackingImage
metadata:
name: parrot-cloned
namespace: longhorn-system
spec:
sourceType: clone
sourceParameters:
backing-image: parrot
encryption: ignore
Important:
backing-image: Specify the name of the backing image to be cloned.encryption: Set the value toignoreto directly clone the backing image. If the value is not given, Longhorn useignoreas default value.
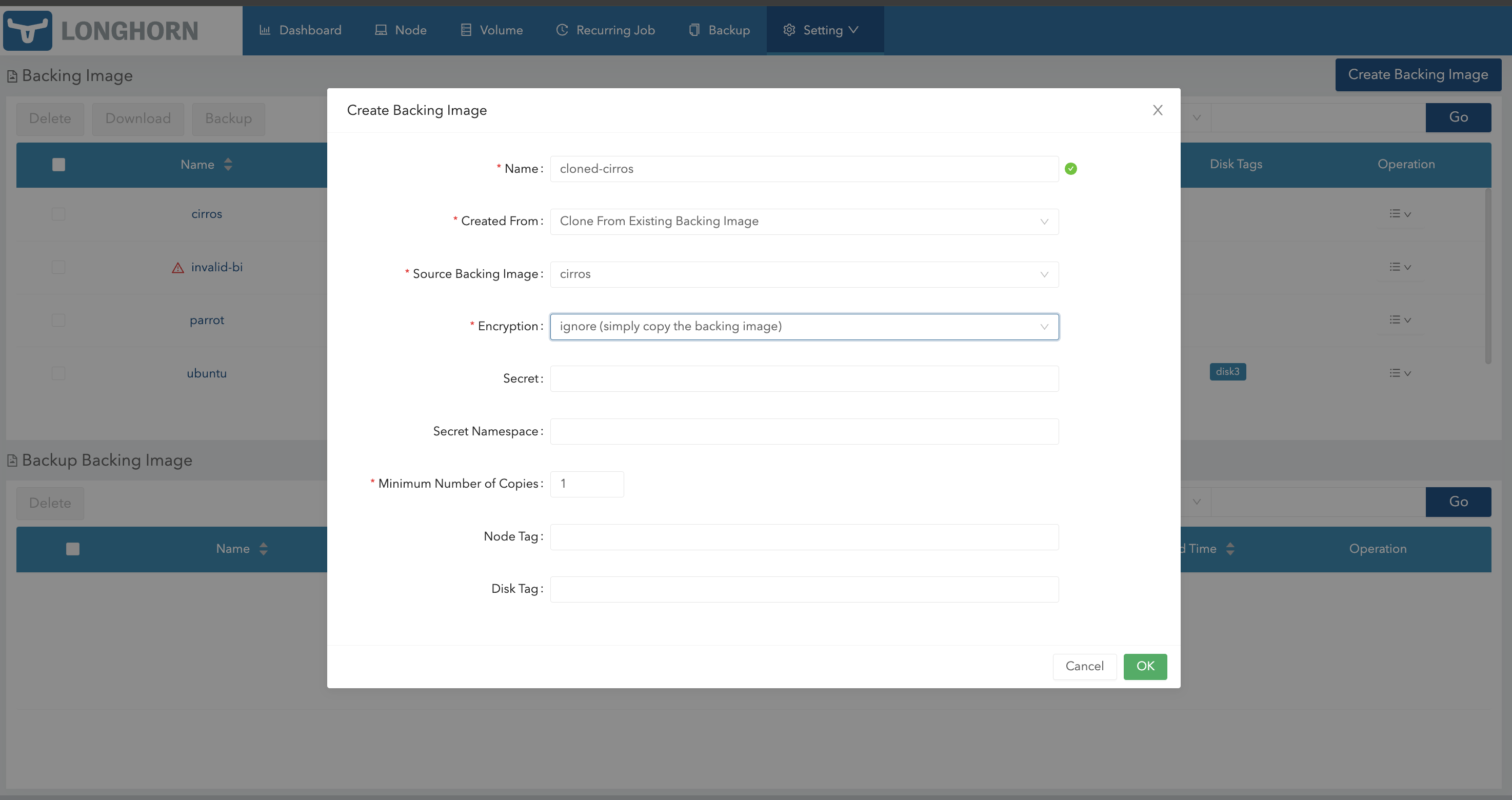
You can also clone a backing image using the Longhorn UI.
- Go to Setting > Backing Image.
- Click Create Backing Image.
- Configure the following settings:
- Created From: Select Clone From Existing Backing Image.
- Encryption: Select Ignore.
- Click OK.
Encrypt a Backing Image
You can enable encryption during cloning of a backing image so that the image can be used with an encrypted volume.
Example of a downloaded backing image:
apiVersion: longhorn.io/v1beta2
kind: BackingImage
metadata:
name: parrot
namespace: longhorn-system
spec:
sourceType: download
sourceParameters:
url: https://longhorn-backing-image.s3-us-west-1.amazonaws.com/parrot.raw
checksum: 304f3ed30ca6878e9056ee6f1b02b328239f0d0c2c1272840998212f9734b196371560b3b939037e4f4c2884ce457c2cbc9f0621f4f5d1ca983983c8cdf8cd9a
Example of YAML code used to clone and encrypt the sample backing image:
apiVersion: longhorn.io/v1beta2
kind: BackingImage
metadata:
name: parrot-cloned-encrypted
namespace: longhorn-system
spec:
sourceType: clone
sourceParameters:
backing-image: parrot
encryption: encrypt
secret: longhorn-crypto
secret-namespace: longhorn-system
Example of YAML code used to encrypt the backing image:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: longhorn-crypto
namespace: longhorn-system
stringData:
CRYPTO_KEY_VALUE: "Your encryption passphrase"
CRYPTO_KEY_PROVIDER: "secret"
CRYPTO_KEY_CIPHER: "aes-xts-plain64"
CRYPTO_KEY_HASH: "sha256"
CRYPTO_KEY_SIZE: "256"
CRYPTO_PBKDF: "argon2i"
Important:
backing-image: Specify the name of the backing image to be cloned.encryption: Set the value toencryptto encrypt the backing image during cloning.secret: Specify the secret used to encrypt the backing image.secret-namespace: Specify the namespace of the secret used to encrypt the backing image.
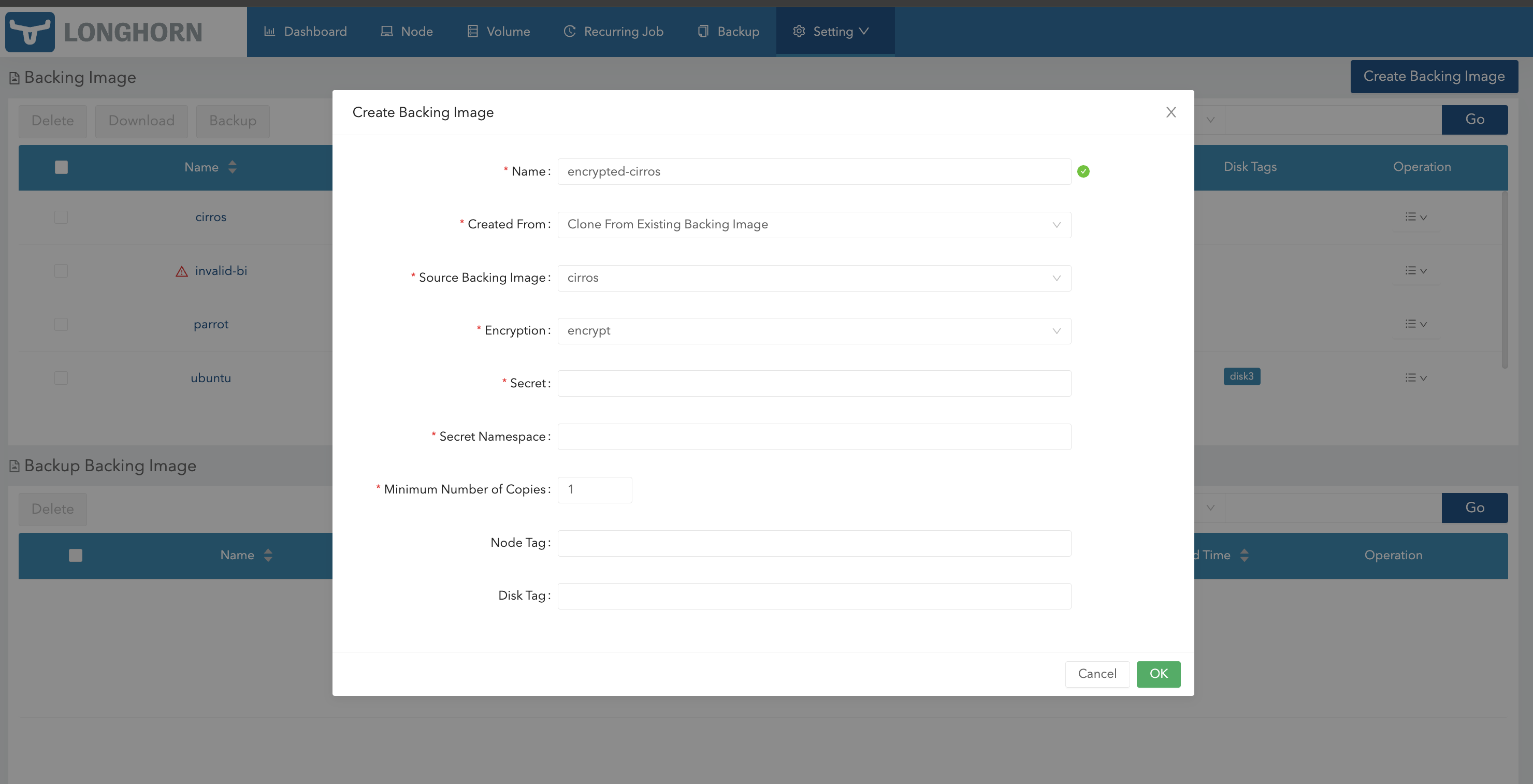
You can also create an encrypted copy of a backing image using the Longhorn UI.
- Go to Setting > Backing Image.
- Click Create Backing Image.
- Configure the following settings:
- Created From: Select Clone From Existing Backing Image.
- Encryption: Select Encrypt.
- Specify the secret and secret namespace to be used for encryption.
- Click OK.
Decrypt a Backing Image
You can decrypt an encrypted backing image through cloning.
Example of an encrypted backing image:
apiVersion: longhorn.io/v1beta2
kind: BackingImage
metadata:
name: parrot-cloned-encrypted
namespace: longhorn-system
spec:
sourceType: clone
sourceParameters:
backing-image: parrot
encryption: encrypt
secret: longhorn-crypto
secret-namespace: longhorn-system
Example of YAML code used to encrypt and decrypt the backing image:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: longhorn-crypto
namespace: longhorn-system
stringData:
CRYPTO_KEY_VALUE: "Your encryption passphrase"
CRYPTO_KEY_PROVIDER: "secret"
CRYPTO_KEY_CIPHER: "aes-xts-plain64"
CRYPTO_KEY_HASH: "sha256"
CRYPTO_KEY_SIZE: "256"
CRYPTO_PBKDF: "argon2i"
Example of YAML code used to decrypt the backing image:
apiVersion: longhorn.io/v1beta2
kind: BackingImage
metadata:
name: parrot-cloned-decrypt
namespace: longhorn-system
spec:
sourceType: clone
sourceParameters:
backing-image: parrot-cloned-encrypted
encryption: decrypt
secret: longhorn-crypto
secret-namespace: longhorn-system
Important:
backing-image: Specify the name of the backing image to be cloned.encryption: Set the value todecryptto decrypt the backing image during cloning.secret: Specify the secret used to decrypt the backing image.secret-namespace: Specify the namespace of the secret used to decrypt the backing image.
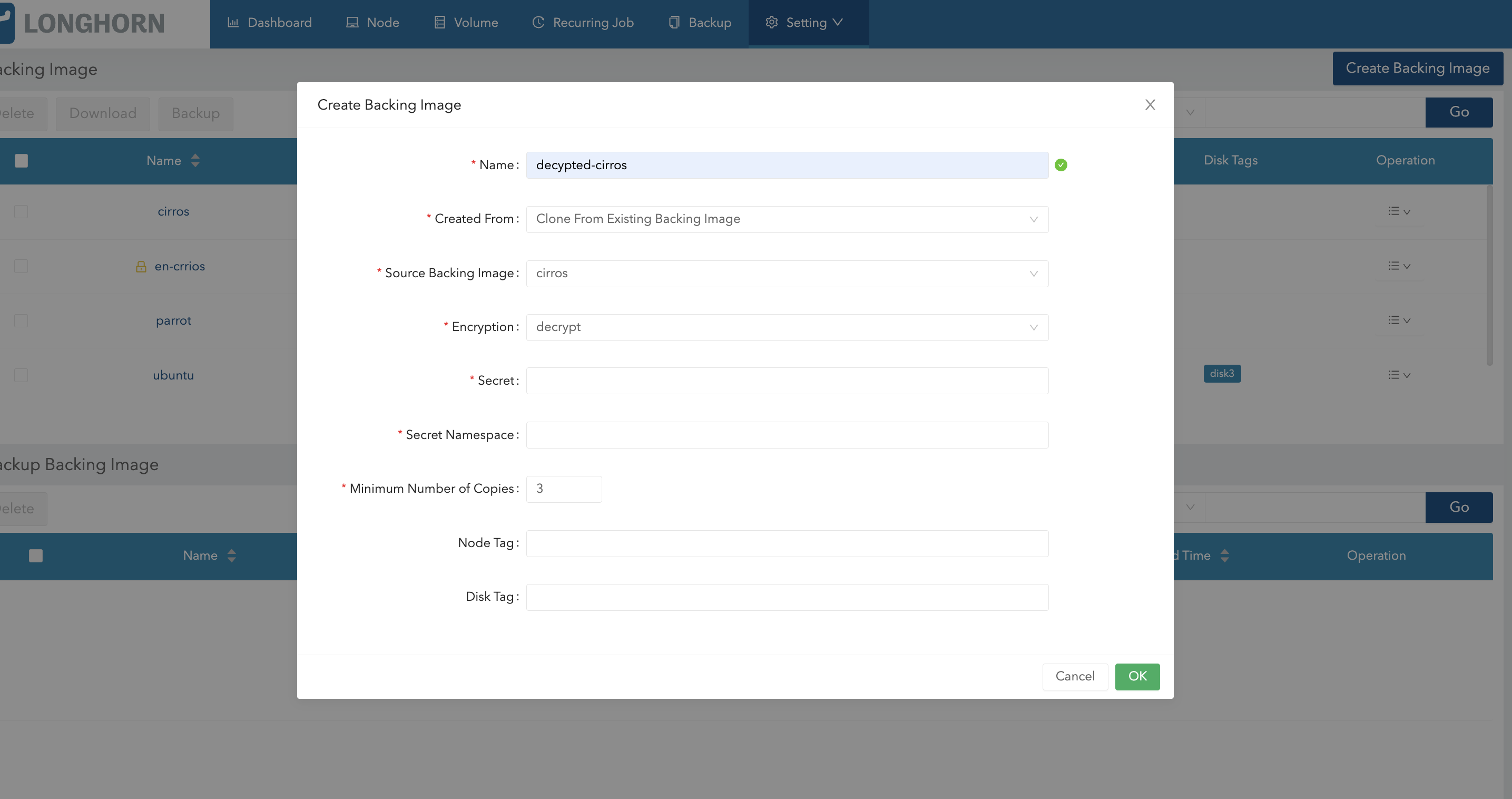
You can also decrypt a backing image (through cloning) using the Longhorn UI.
- Go to Setting > Backing Image.
- Click Create Backing Image.
- Configure the following settings:
- Created From: Select Clone From Existing Backing Image.
- Encryption: Select Decrypt.
- Specify the secret and secret namespace to be used for decryption.
- Click OK.
Use an Encrypted Backing Image with an Encrypted Volume
The secret used to encrypt the backing image and the volume must be identical. Once the encrypted backing image is ready, you can create the StorageClass with the corresponding backing image and the secret to create the volume for the workload.
Example of YAML code for the encryption secret:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: longhorn-crypto
namespace: longhorn-system
stringData:
CRYPTO_KEY_VALUE: "Your encryption passphrase"
CRYPTO_KEY_PROVIDER: "secret"
CRYPTO_KEY_CIPHER: "aes-xts-plain64"
CRYPTO_KEY_HASH: "sha256"
CRYPTO_KEY_SIZE: "256"
CRYPTO_PBKDF: "argon2i"
Example of YAML code for the StorageClass:
kind: StorageClass
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: longhorn-crypto-global
provisioner: driver.longhorn.io
allowVolumeExpansion: true
parameters:
numberOfReplicas: "3"
staleReplicaTimeout: "2880" # 48 hours in minutes
fromBackup: ""
encrypted: "true"
backingImage: "parrot-cloned-encrypted"
backingImageDataSourceType: "clone"
# global secret that contains the encryption key that will be used for all volumes
csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-name: "longhorn-crypto"
csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-namespace: "longhorn-system"
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-publish-secret-name: "longhorn-crypto"
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-publish-secret-namespace: "longhorn-system"
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-name: "longhorn-crypto"
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-namespace: "longhorn-system"
For more information, see Volume Encryption.
Limitations
- Longhorn is unable to encrypt backing images that are already encrypted, and decrypt backing images that are not encrypted.
- Longhorn does not allow you to change the encryption key of an encrypted backing image.
- When encrypting a qcow2 image, Longhorn first creates a raw image from the qcow2 image and then encrypts it. The resulting encrypted raw image temporarily consumes extra space during cloning. For example,
- If we encrypt a 10MiB qcow2 image with a virtual size of 200MiB, we first create the raw image from the qcow2 which will consume 200MiB of the space.
- Longhorn then create the encrypted backing image from that 200MiB raw image which will take another 200MiB of the space.
- After the encrypted backing image is created, the temporary raw image will be cleaned up and free the 200MiB from the space.
- If the source backing image is a sparse file, the file loses its sparsity after encryption.
- To allow storage of the LUKS metadata during encryption, the image size is increased by 16 MB. For more information, see the cryptsetup release notes.
© 2019-2026 Longhorn Authors | Documentation Distributed under CC-BY-4.0
© 2026 The Linux Foundation. All rights reserved. The Linux Foundation has registered trademarks and uses trademarks. For a list of trademarks of The Linux Foundation, please see our Trademark Usage page.