Create a Snapshot
A snapshot is the state of a Kubernetes volume at any given moment in time.
Snapshot Management via UI
To create a snapshot of an existing cluster, follow these steps:
- In the top navigation bar of the Longhorn UI, click Volume.
- Click the name of the volume for which you want to create a snapshot. This leads to the volume detail page.
- Click the Take Snapshot button.
Once the snapshot is created, you will see it in the list of snapshots for the volume before the Volume Head.
Understanding the Snapshot Chain Visualization
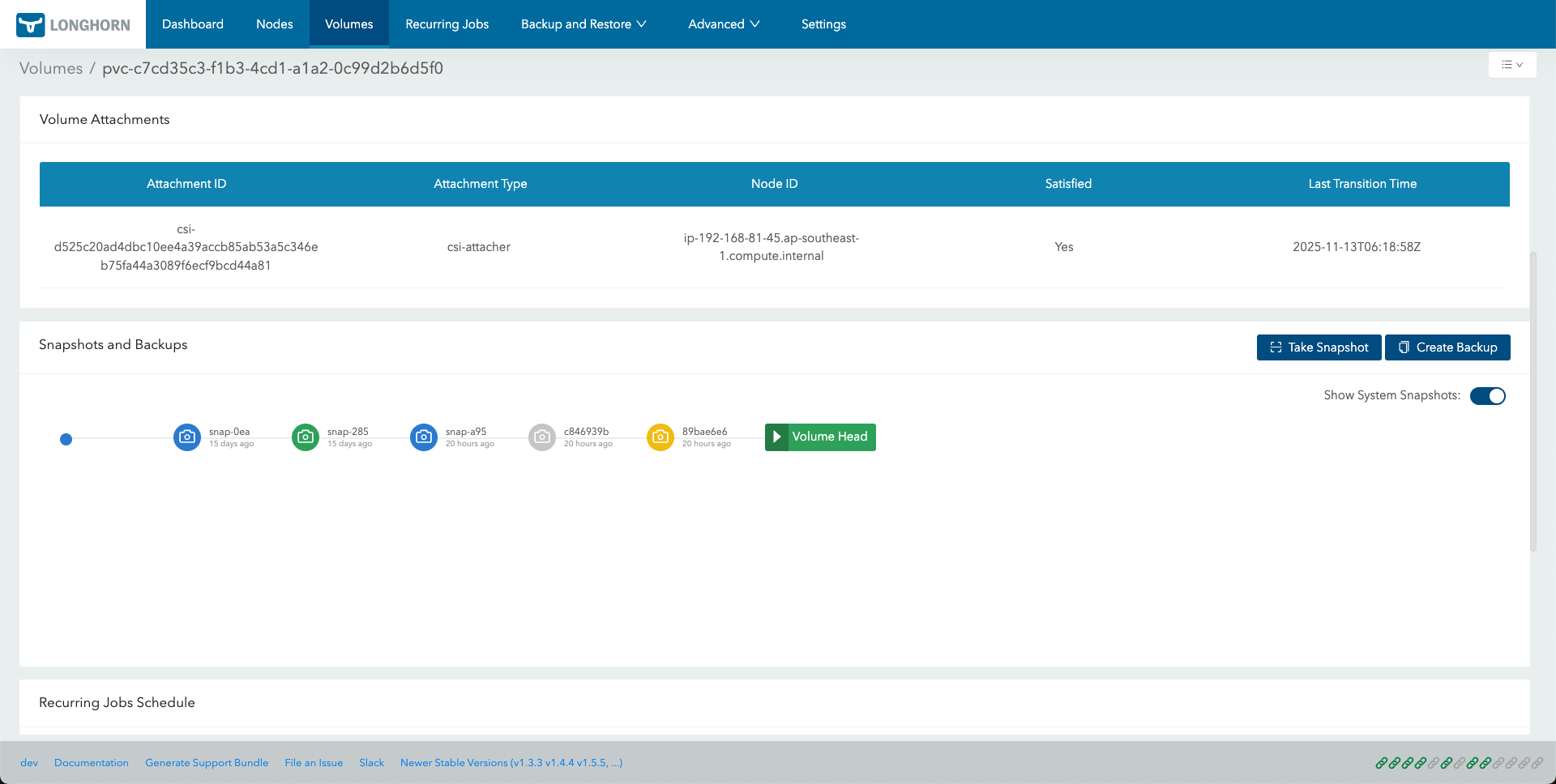
On the Volume Details page, the Snapshots and Backups section displays the snapshot history as a chain. By default, the Show System Snapshots option is enabled, meaning all system-created snapshots are displayed automatically.
Each snapshot in the chain is color-coded to indicate its type or status, following a specific priority (highest status is displayed if multiple apply).
| Snapshot Type | Color | Description | Priority (1 = Highest) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Error | Red | Indicates a snapshot that failed during creation or has an issue. | 1 |
| Removed | Light Grey | A snapshot that has been marked for removal or successfully deleted. | 2 |
| System-created | Orange/Yellow | Snapshots automatically created by Longhorn, often for recurring jobs or internal operations. | 3 |
| Backup | Green | A snapshot that has been backed up to a configured backup target. | 4 |
| Default (User-created) | Blue | A standard, user-initiated snapshot taken manually using the Take Snapshot button. | 5 |
| Below is an example of the snapshot chain visualization: |
Snapshot Management with Custom Resources (CRs)
This section demonstrates how to create, list, restore, and delete Longhorn snapshots directly via kubectl using Longhorn’s Custom Resources (CRs).
Note: Longhorn uses its own
SnapshotCRD under thelonghorn.ioAPI group (for example,v1beta2), not the generic KubernetesVolumeSnapshotfromsnapshot.storage.k8s.io.
Create a Snapshot
Prepare the manifest: Create a file named
longhorn-snapshot.yaml:apiVersion: longhorn.io/v1beta2 kind: Snapshot metadata: name: longhorn-test-snapshot namespace: longhorn-system spec: volume: pvc-840804d8-6f11-49fd-afae-54bc5be639de # replace with your actual Longhorn volume name createSnapshot: trueApply the manifest:
kubectl apply -f longhorn-snapshot.yamlExpected output:
snapshot.longhorn.io/longhorn-test-snapshot createdNote: If the volume is detached, you will see a brief warning about the engine not running. Longhorn automatically retries, and the snapshot will complete once the volume is attached.
List Snapshots
kubectl get snapshots.longhorn.io -l longhornvolume=pvc-840804d8-6f11-49fd-afae-54bc5be639de -n longhorn-system
Delete a Snapshot
kubectl delete snapshot.longhorn.io longhorn-test-snapshot -n longhorn-system
Expected output:
snapshot.longhorn.io "longhorn-test-snapshot" deleted
Note: Longhorn automatically handles the cleanup of the underlying data.
Data Engine Behavioral Differences
When deleting a snapshot that is the direct parent of the Volume Head (the current active state), the behavior of the Snapshot Custom Resource (CR) depends on the Data Engine being used:
| Behavior | v1 Data Engine | v2 Data Engine |
|---|---|---|
| CR Persistence | The Snapshot CR remains in the system. | The Snapshot CR is immediately removed. |
| Status Fields | READYTOUSE becomes false and the snapshot is marked as Removed. | Not applicable, because the Snapshot CR is deleted. |
| Explanation | v1 volumes cannot physically merge the parent of a live volume head immediately. The CR remains to track the snapshot data until a later merge or cleanup operation. | v2 volumes support live merging of the parent snapshot into the volume head, allowing for immediate cleanup of both data and metadata. |
This behavioral difference is expected. In v2 volumes, the immediate disappearance of the Snapshot CR indicates that the engine has successfully finalized the deletion and merged the data.
© 2019-2026 Longhorn Authors | Documentation Distributed under CC-BY-4.0
© 2026 The Linux Foundation. All rights reserved. The Linux Foundation has registered trademarks and uses trademarks. For a list of trademarks of The Linux Foundation, please see our Trademark Usage page.